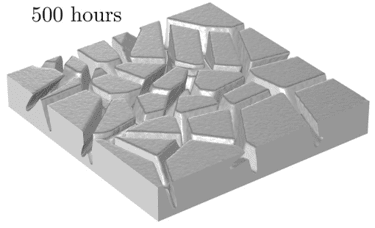
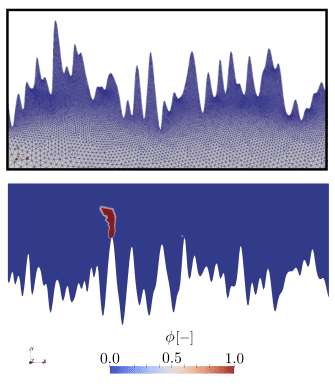
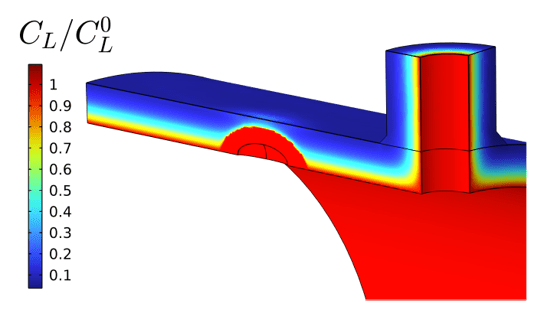
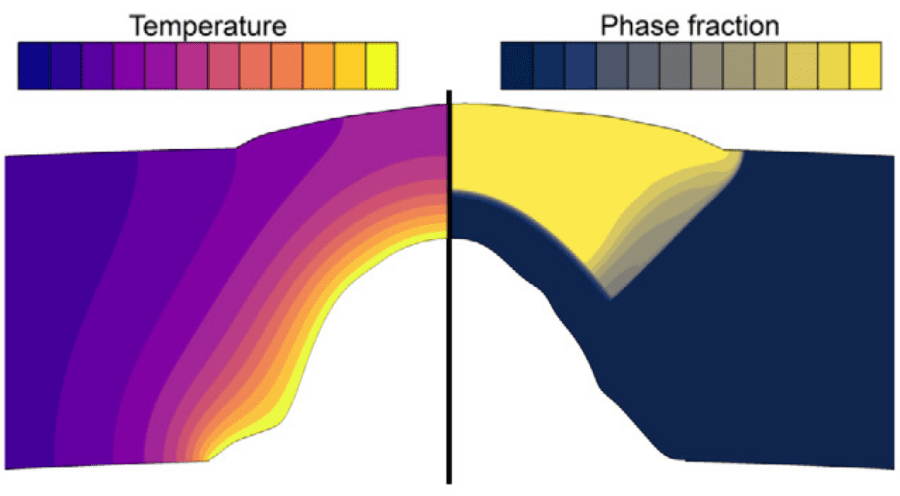
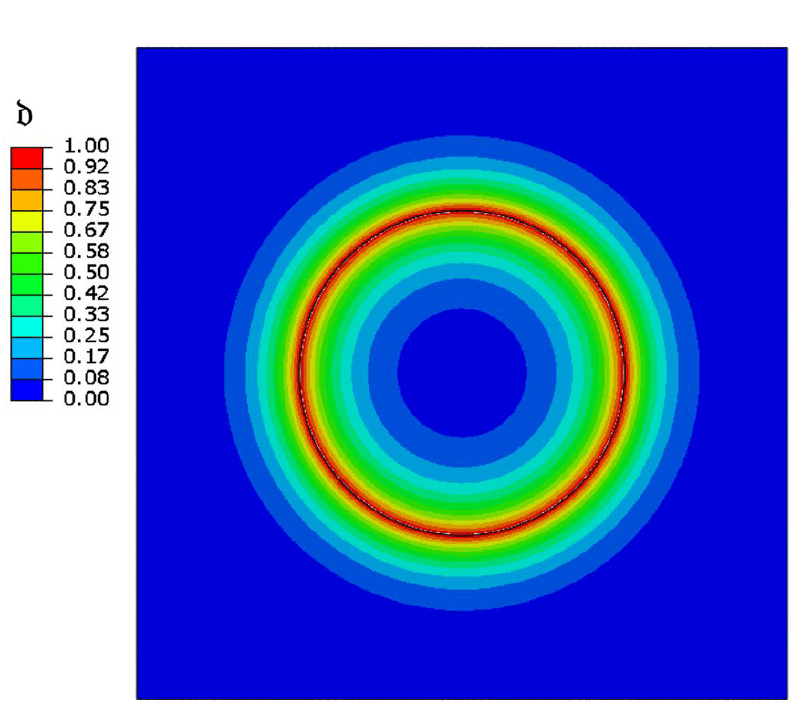
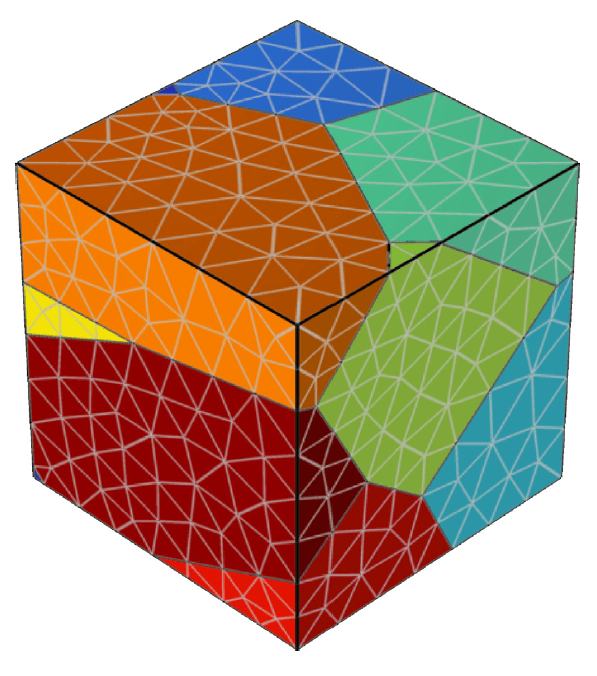
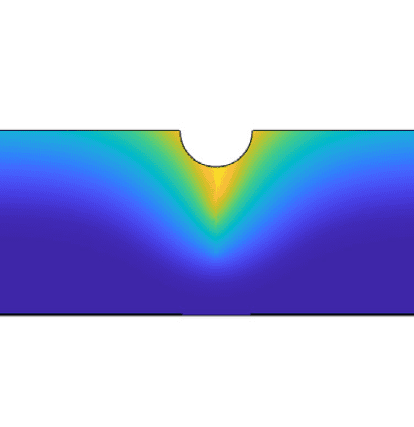
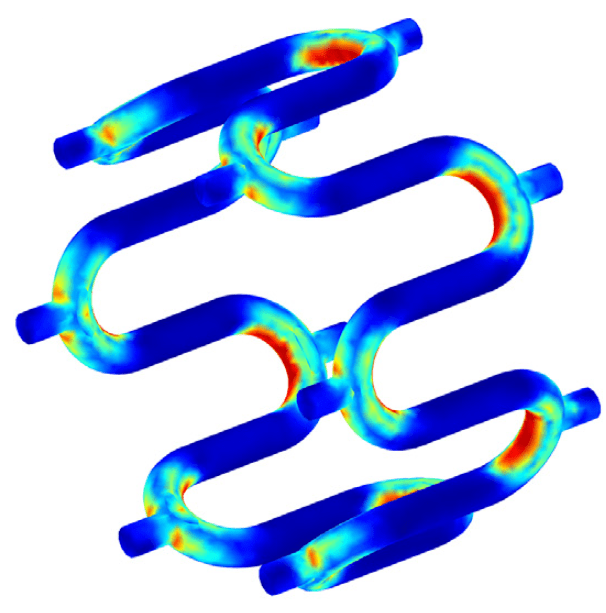
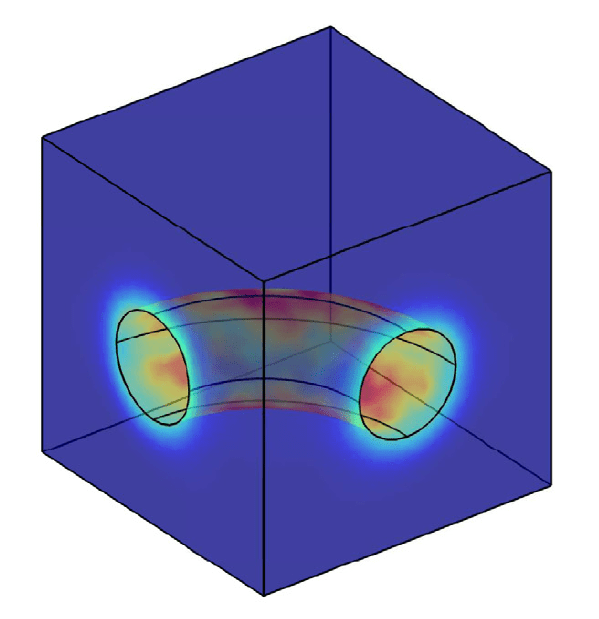
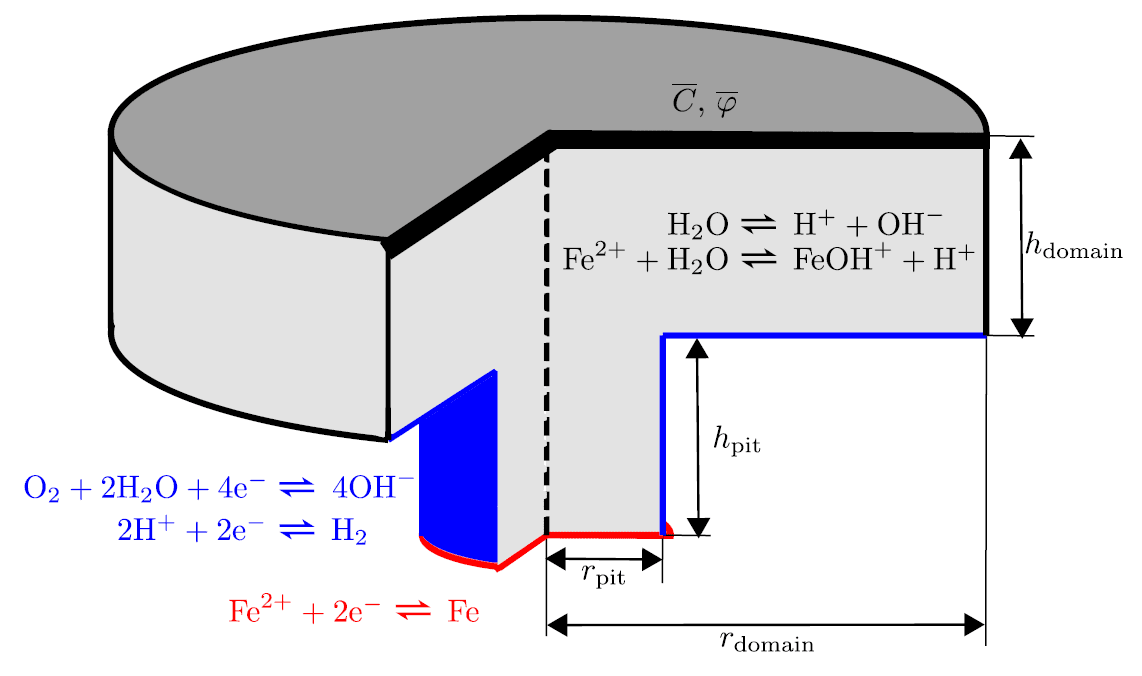
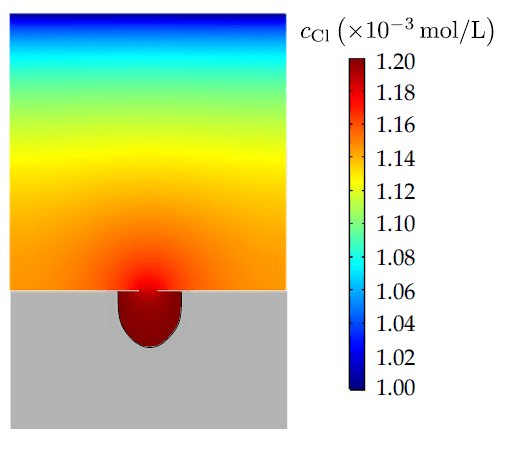
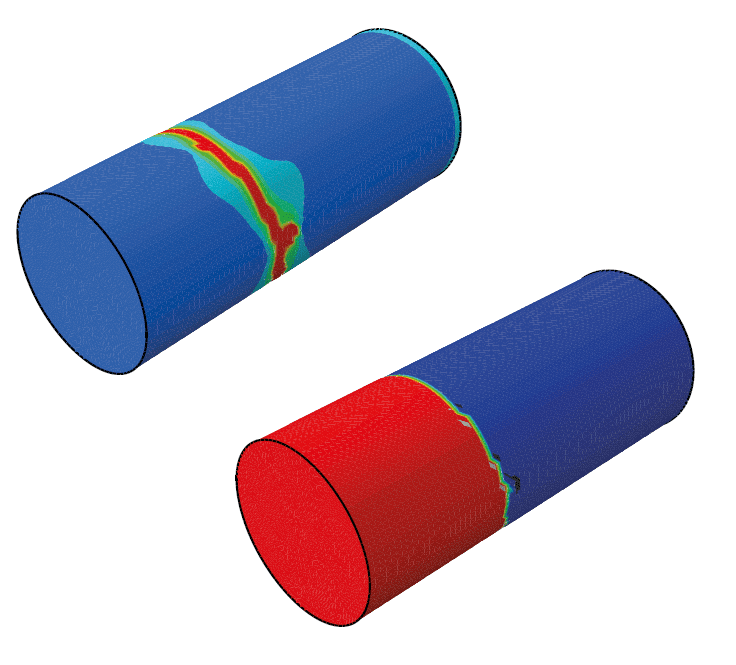
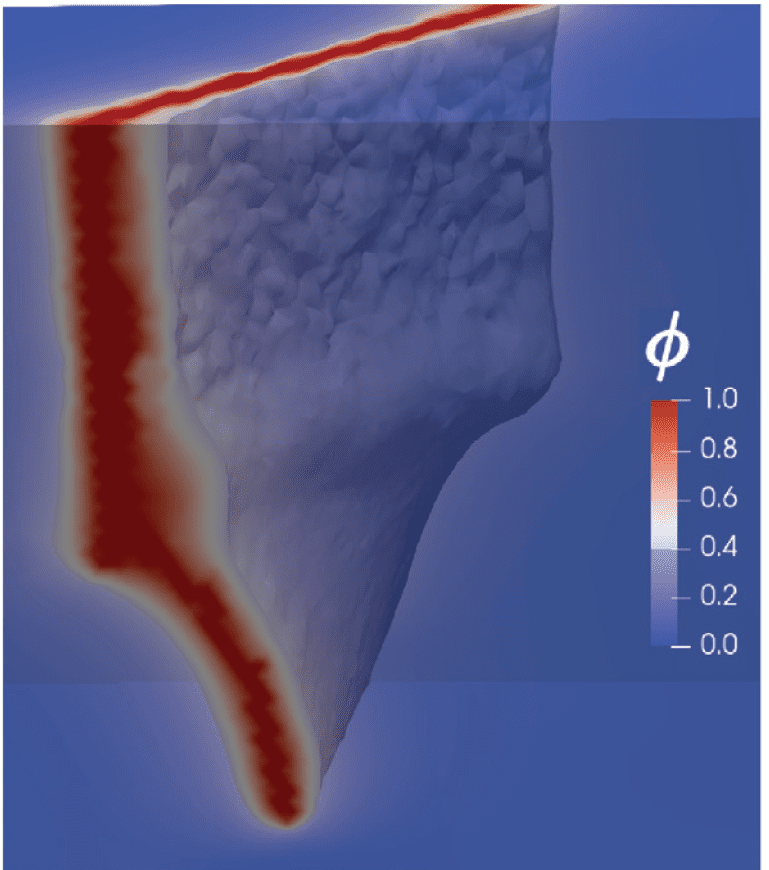
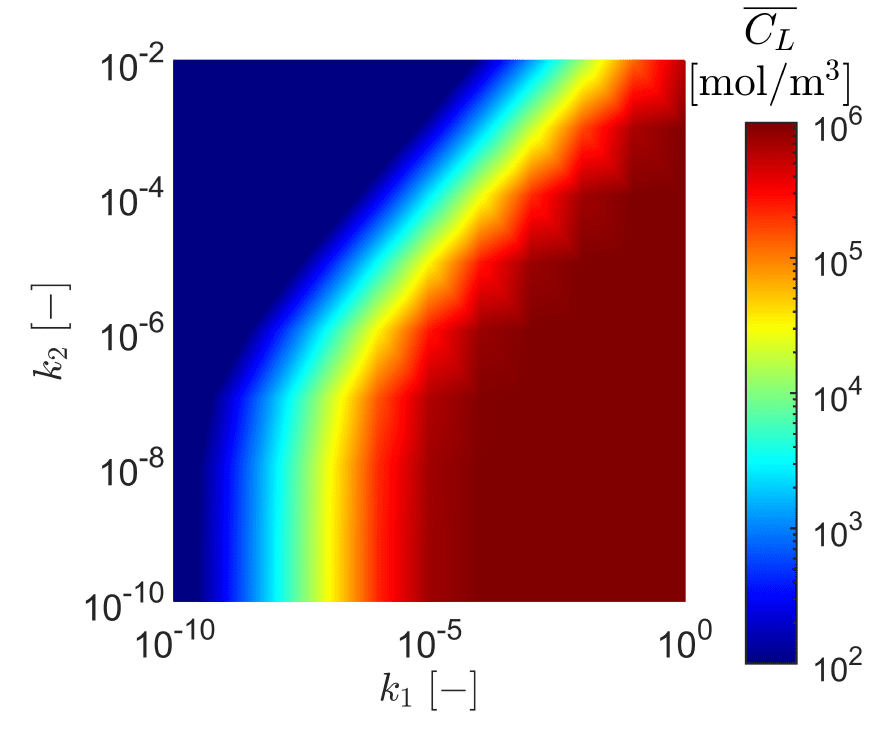
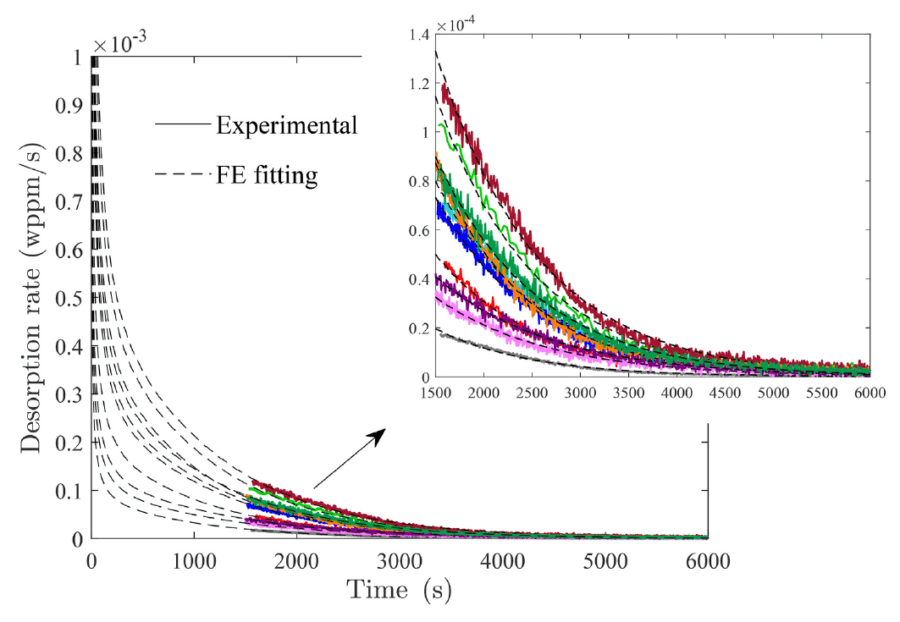
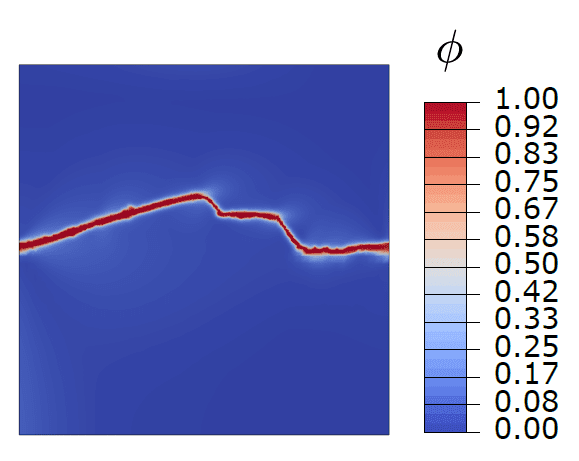
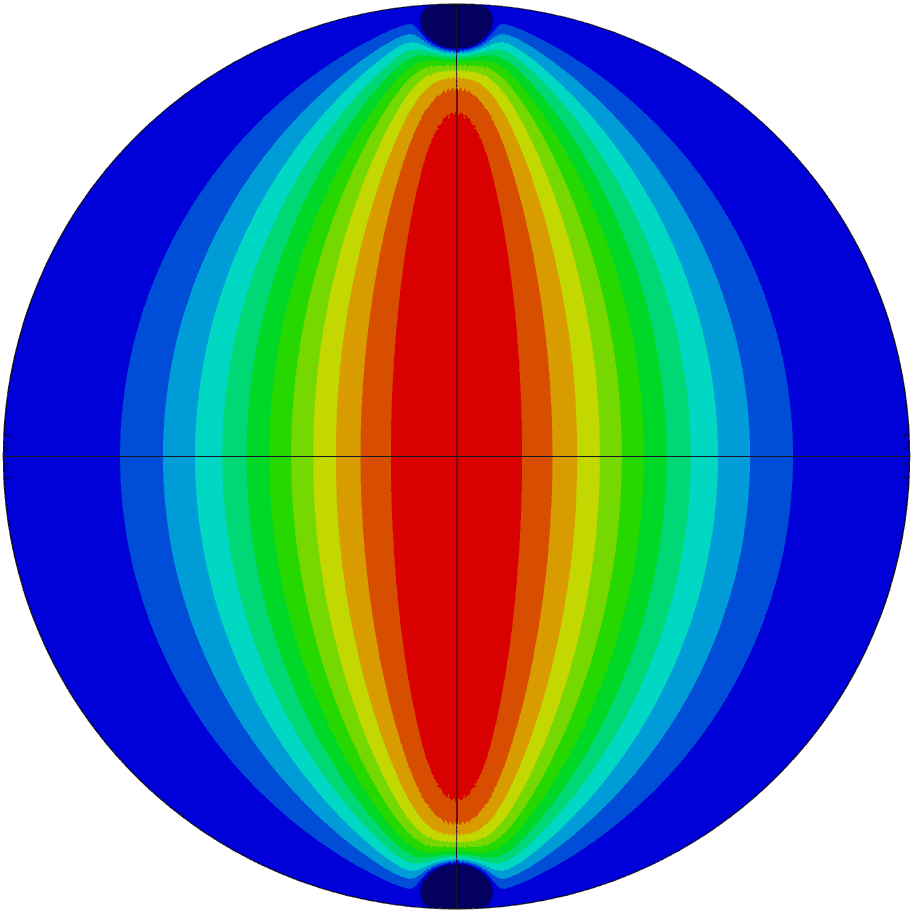
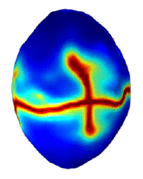
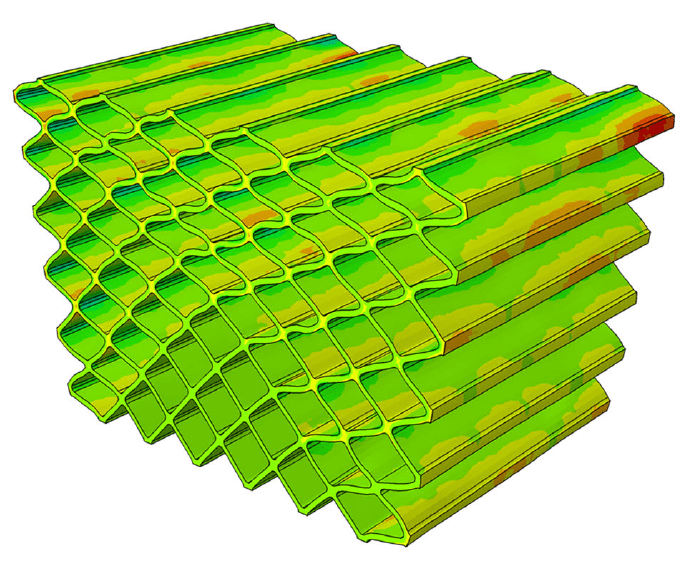
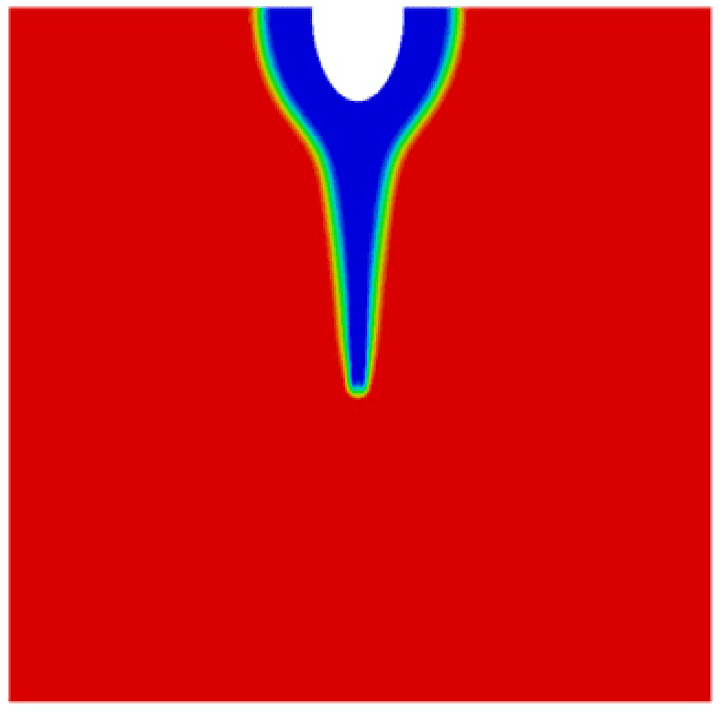
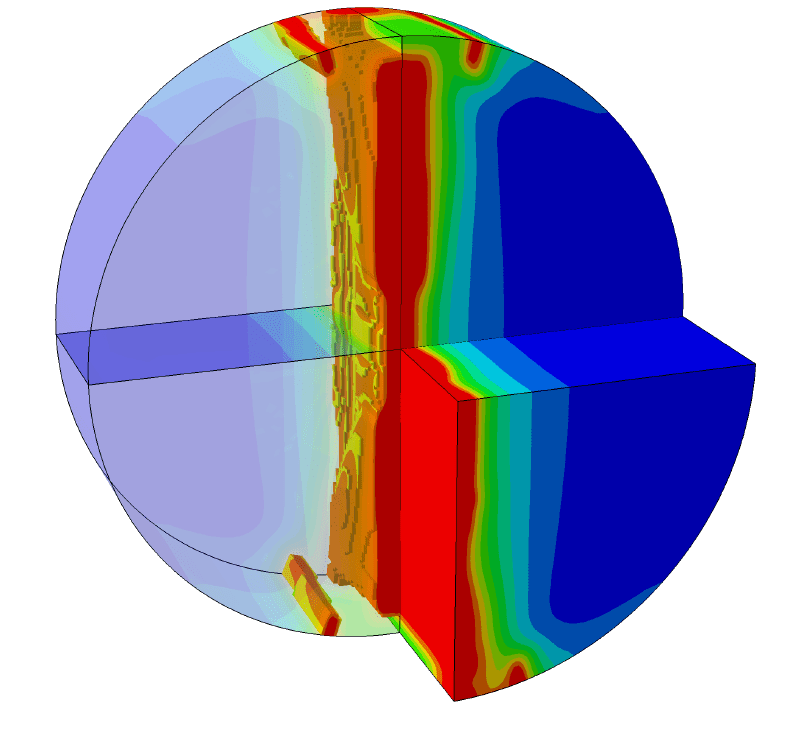
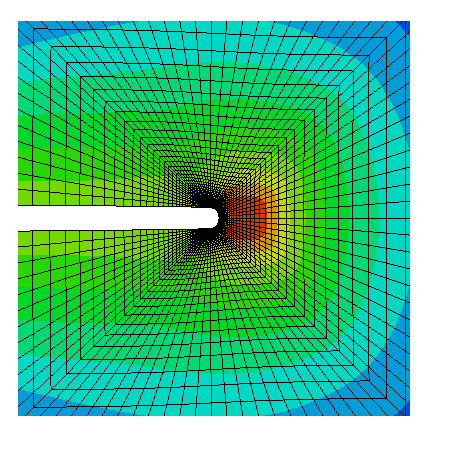
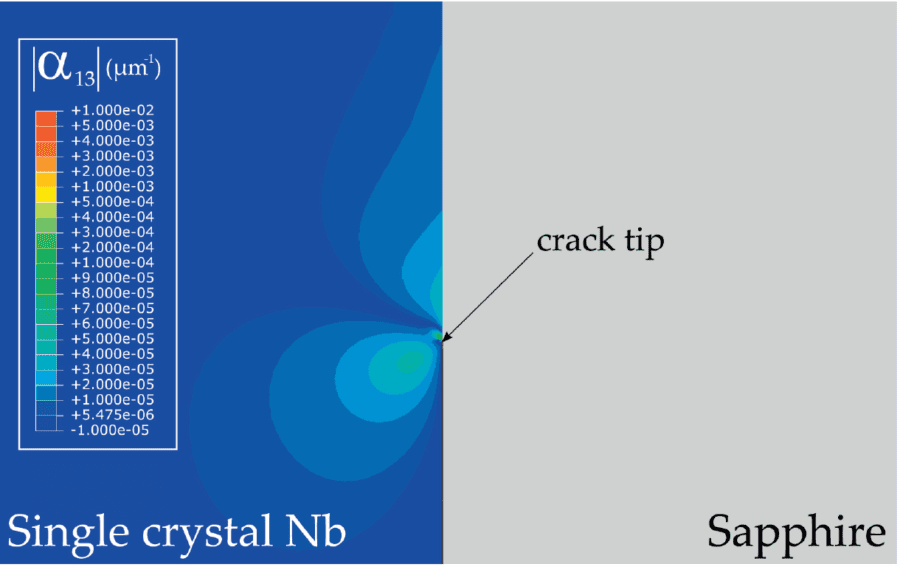
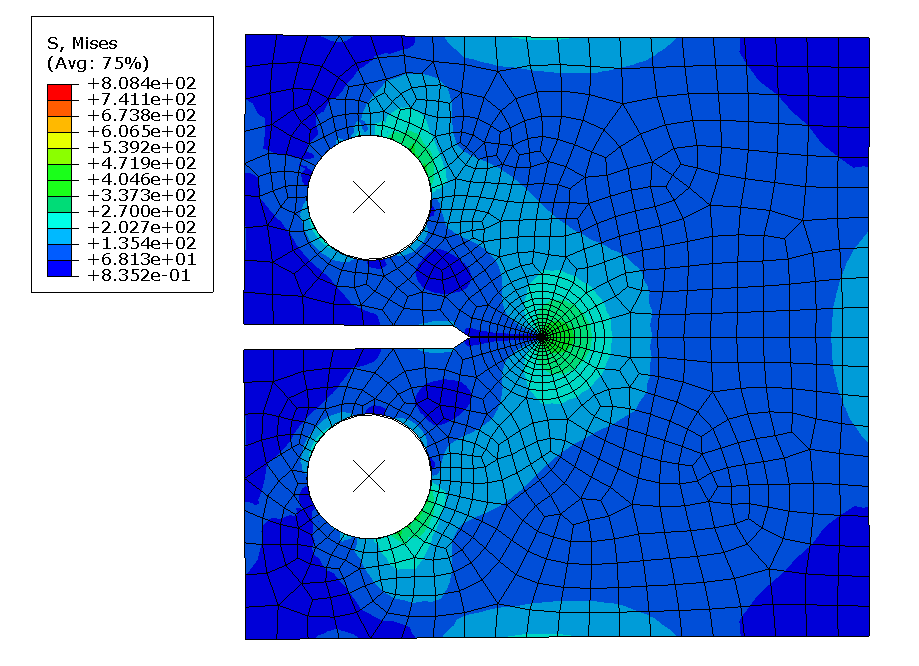
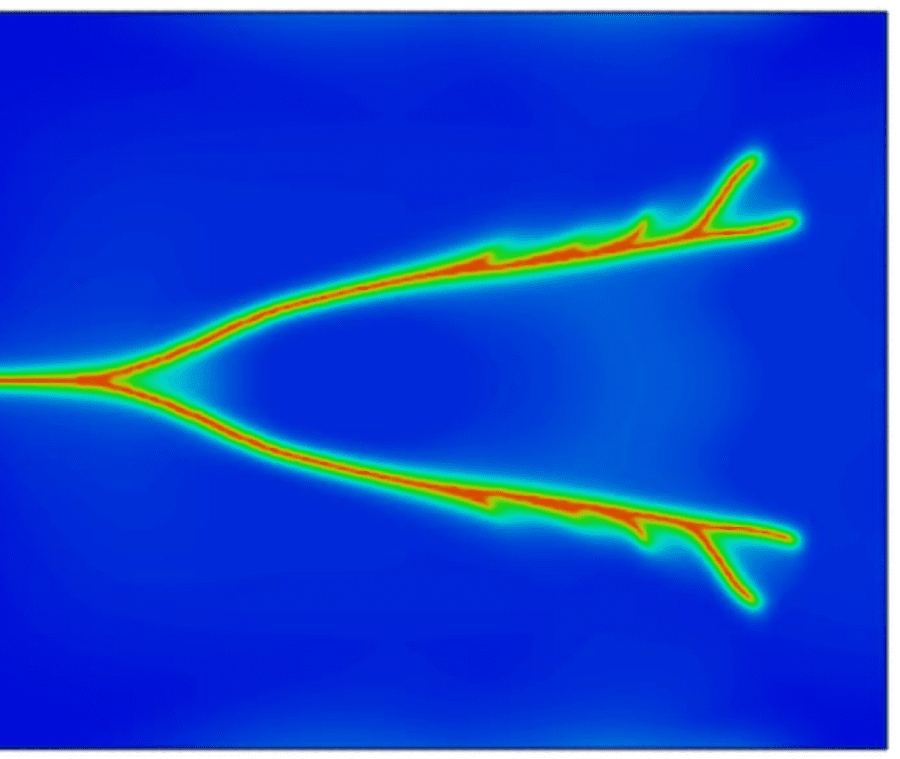
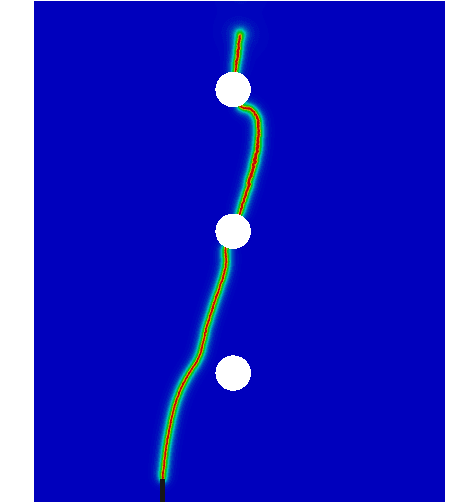
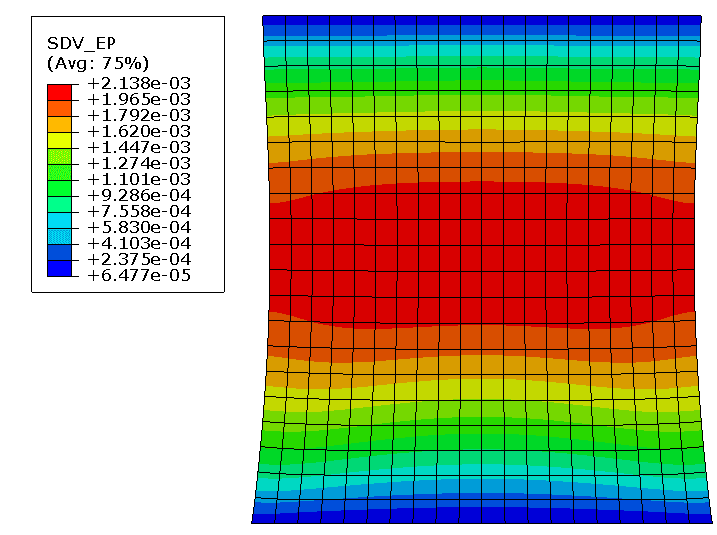
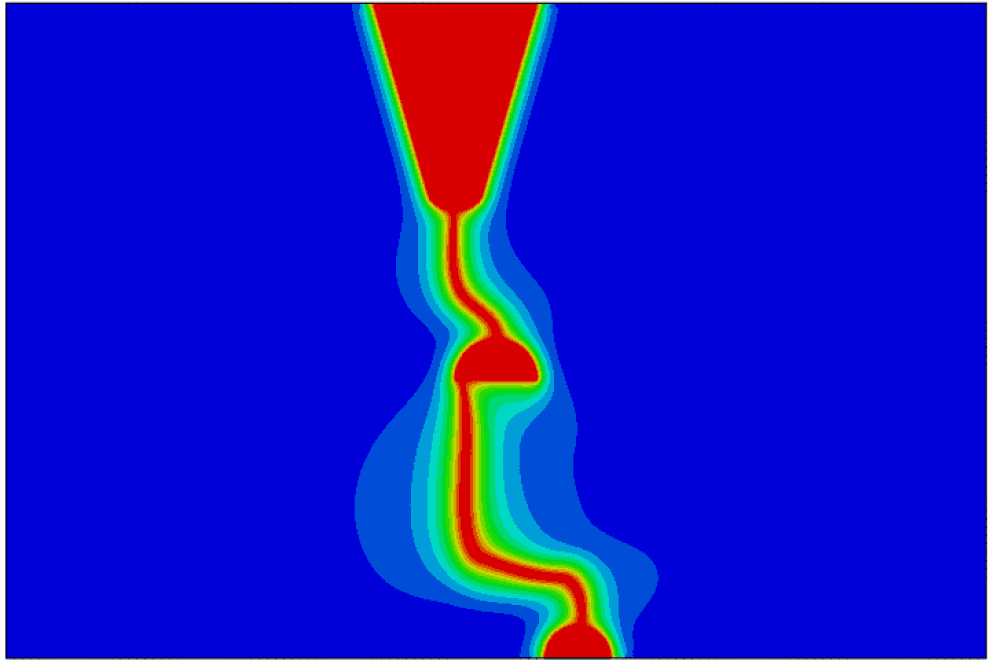
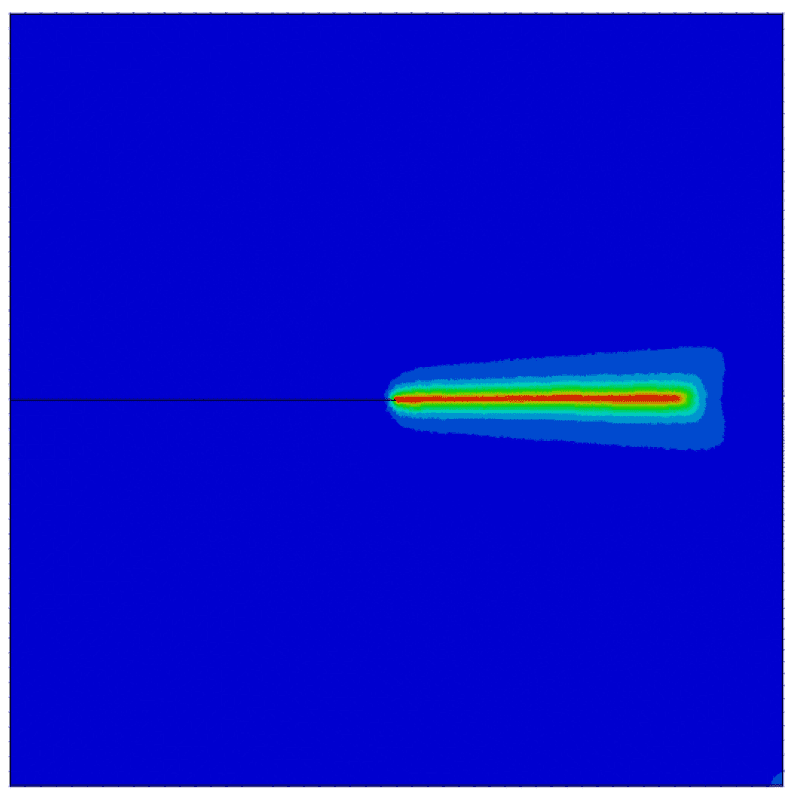
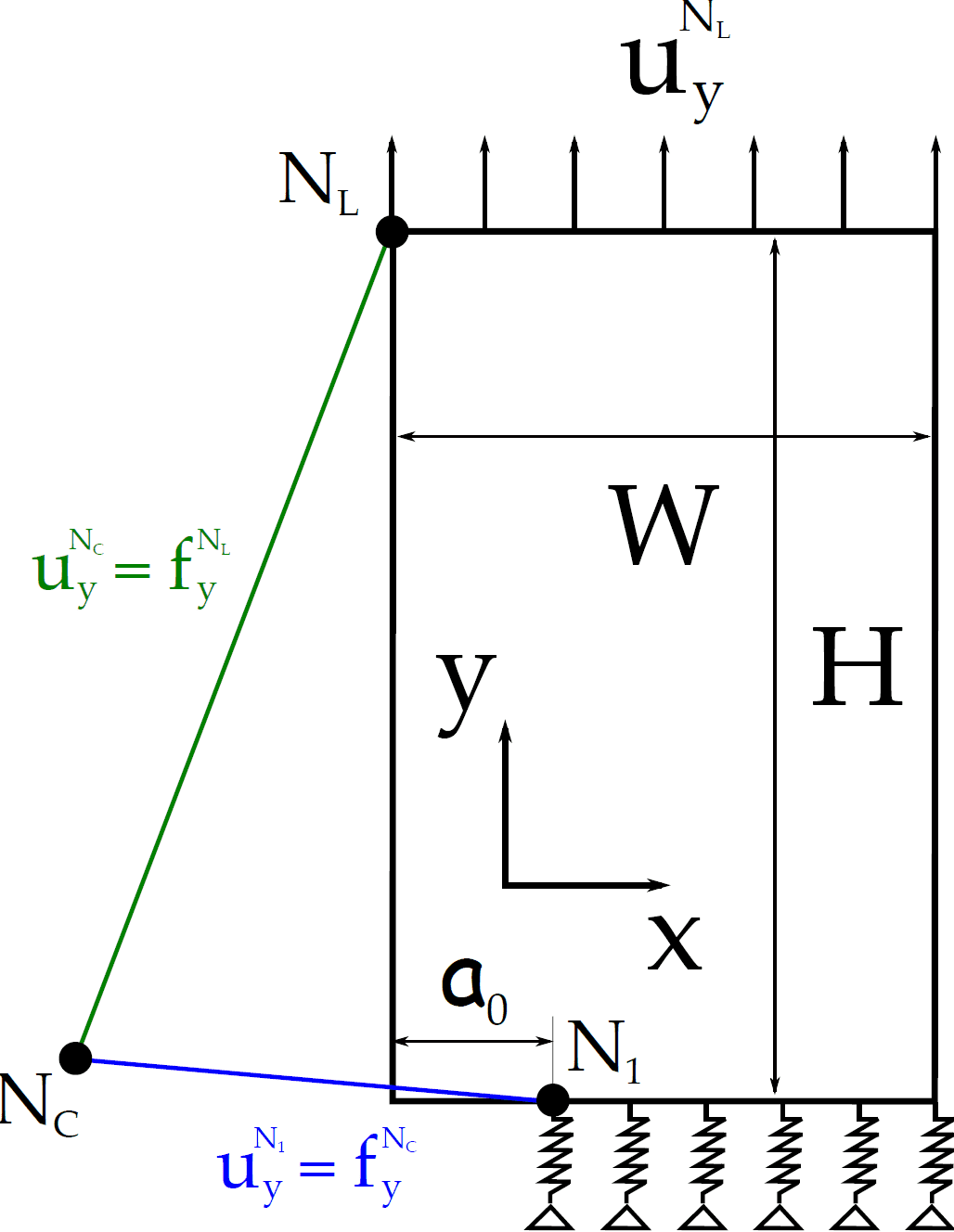
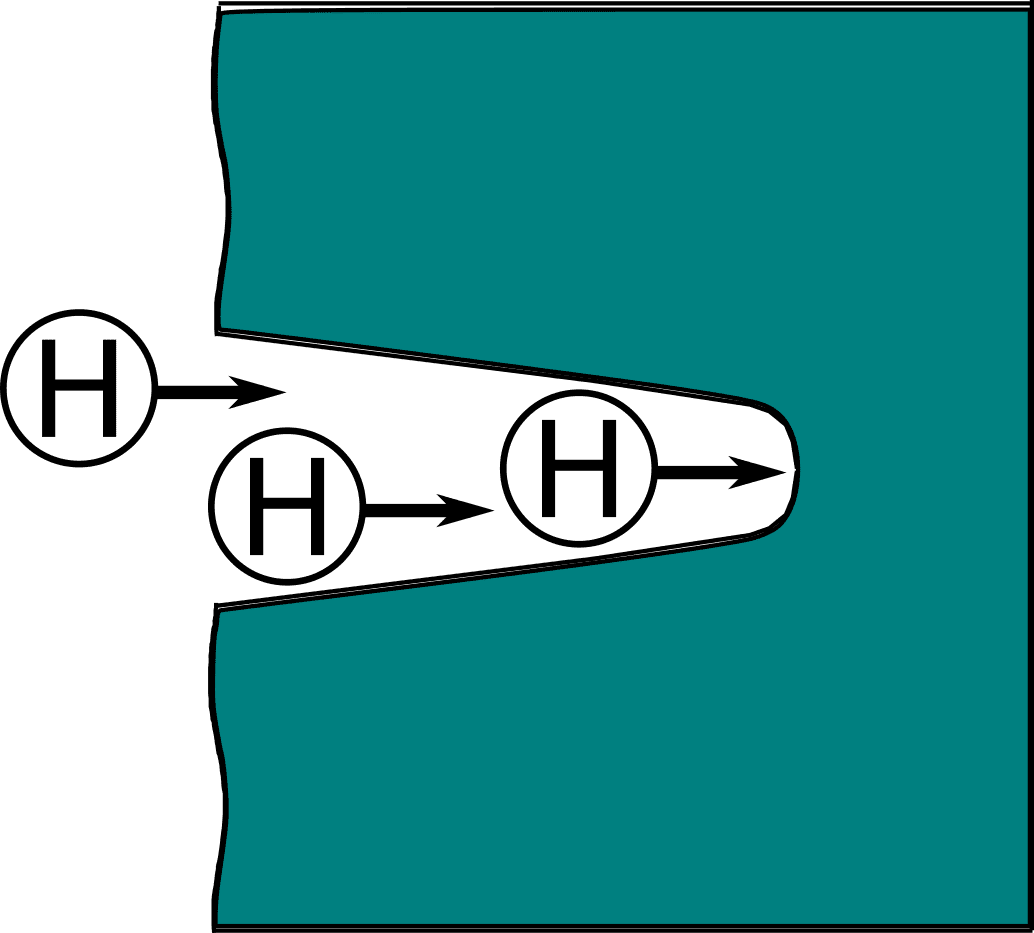
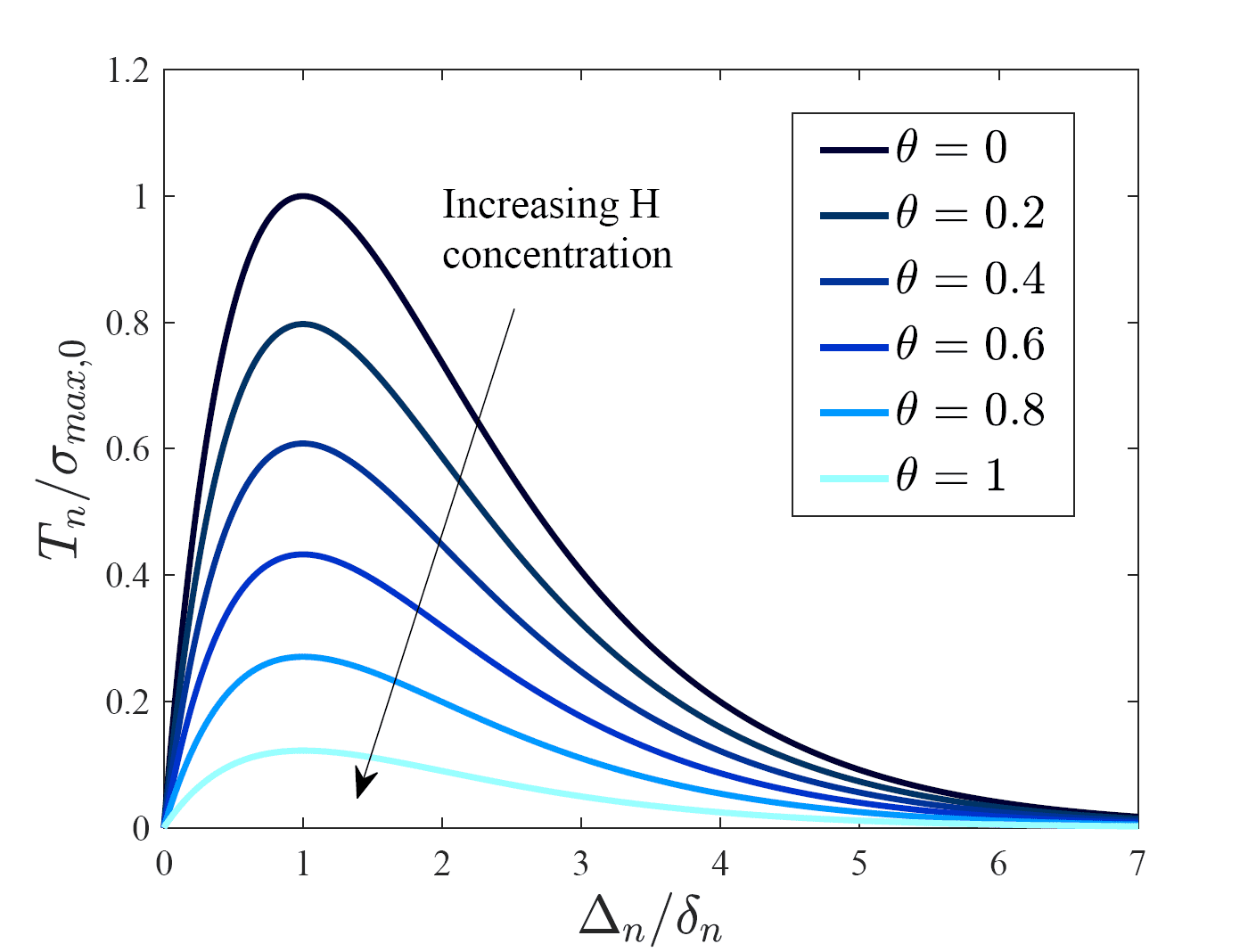
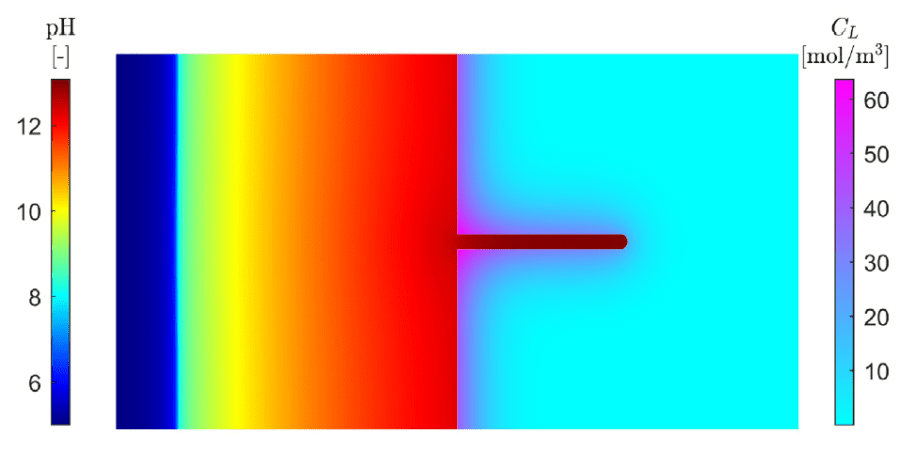COMSOL implementation of phase field corrosion for intergranular (IG) corrosion.
Paper: A. Lhoest, S. Kovacevic, D. Nguyen-Manh, J. Lim, E. Martínez-Pañeda, M. Wenman. A mesoscale phase-field model of intergranular liquid lithium corrosion of ferritic/martensitic steels. npj Materials Degradation 9, 68 (2025)